Оn-chain Government Experiment
At present, Polkadot is one of the largest DAOs in the world! There are many interesting events
taking place in the ecosystem as part of the on-chain governance experiment.
Robonomics developers suggest that hackathon participants increase the level of Polkadot community
immersion by integrating events related to voting, new treasury requests, epoch
changes, and much more, into a typical smart home system.
This article discusses smart home management through the Robonomics Cloud as a result of any event in the Polkadot ecosystem. Here is an example of how a lamp can be turned on when a new referendum is being submitted in the Polkadot network.
Requirements
- Installed Home Assistant instance with Robonomics integration. Installation methods can be found here.
- Polkadot node or gateway for interaction. For example -
wss://polkadot.api.onfinality.io - Robonomics node or gateway for interaction.
- Created account in ED25519 format. Information can be found here.
- Having created account in a device list of the Robonomics subscription. Learn more here.
- Subscription owner and controller addresses.
Python libraries:
Creating a Polkadot Listener
First, you need to create a script that will listen for new events in the Polkadot network. In the example, we will track the creation of new Referenda.
For testing convenience, a local Polkadot node in dev mode was used.You may find deployment manual here.
To connect to a public node, change the “POLKADOT_GATEWAY” variable.
Example code:
from substrateinterface import SubstrateInterface
POLKADOT_GATEWAY = "ws://127.0.0.1:9944"
substrate = SubstrateInterface(
url=POLKADOT_GATEWAY
)
def subscription_handler(data, update_nr, subscription_id):
if update_nr == 0:
print('Referenda count start:', data.value)
if update_nr > 0:
print('Referenda count increased:', data.value)
substrate.query("Referenda", "ReferendumCount", subscription_handler=subscription_handler)This script will listen for changes in the current referendum number and display the number of the latest referendum.
Testing
Run the program and open polkadot.js.
To switch to the local dev node, click on the icon in the upper left corner, and a sidebar menu will appear. Select “Development” and “Local Node” at the bottom, then click “Switch”.
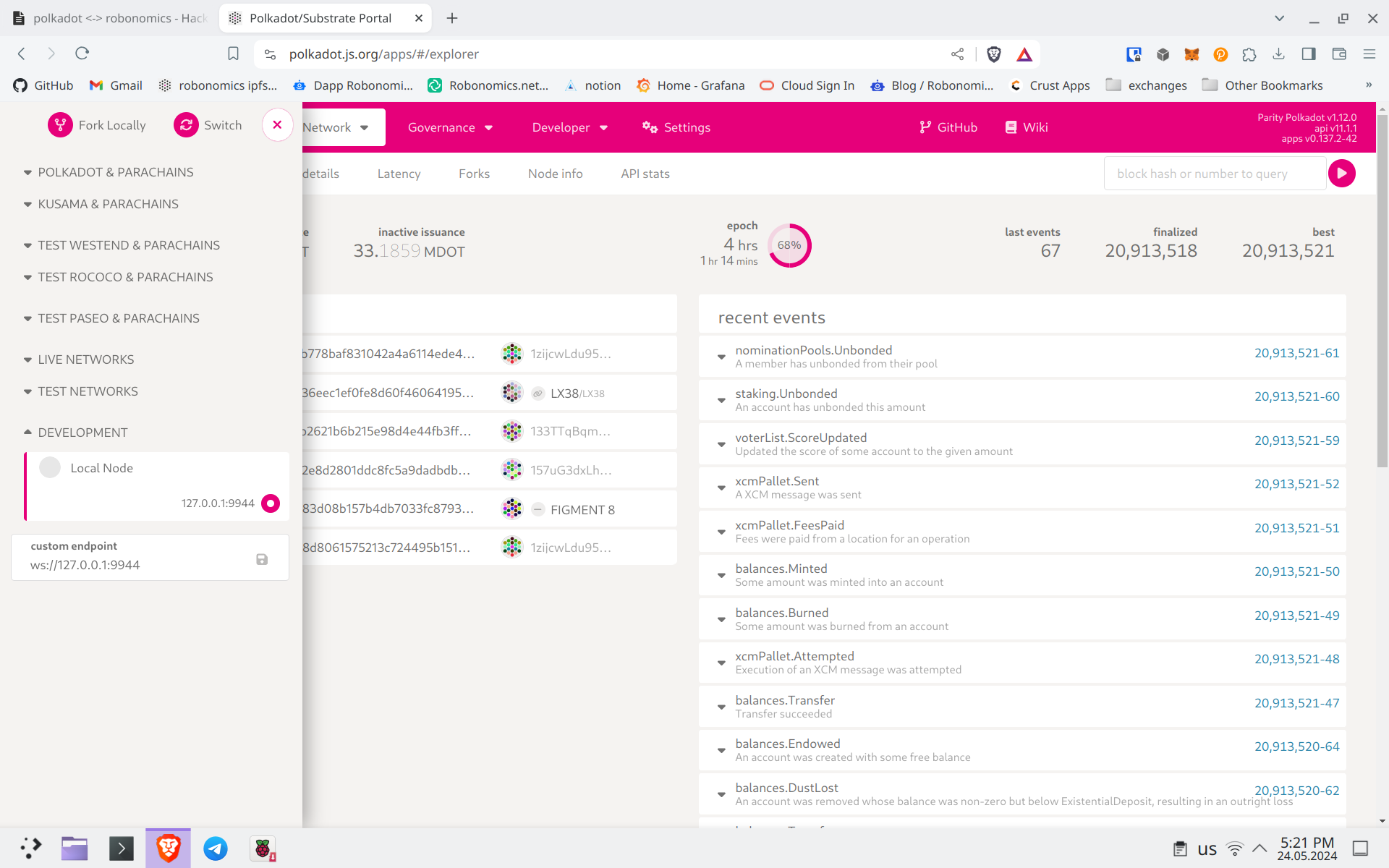
You will switch to the local node. Go to the “Governance” -> “Preimages” tab.
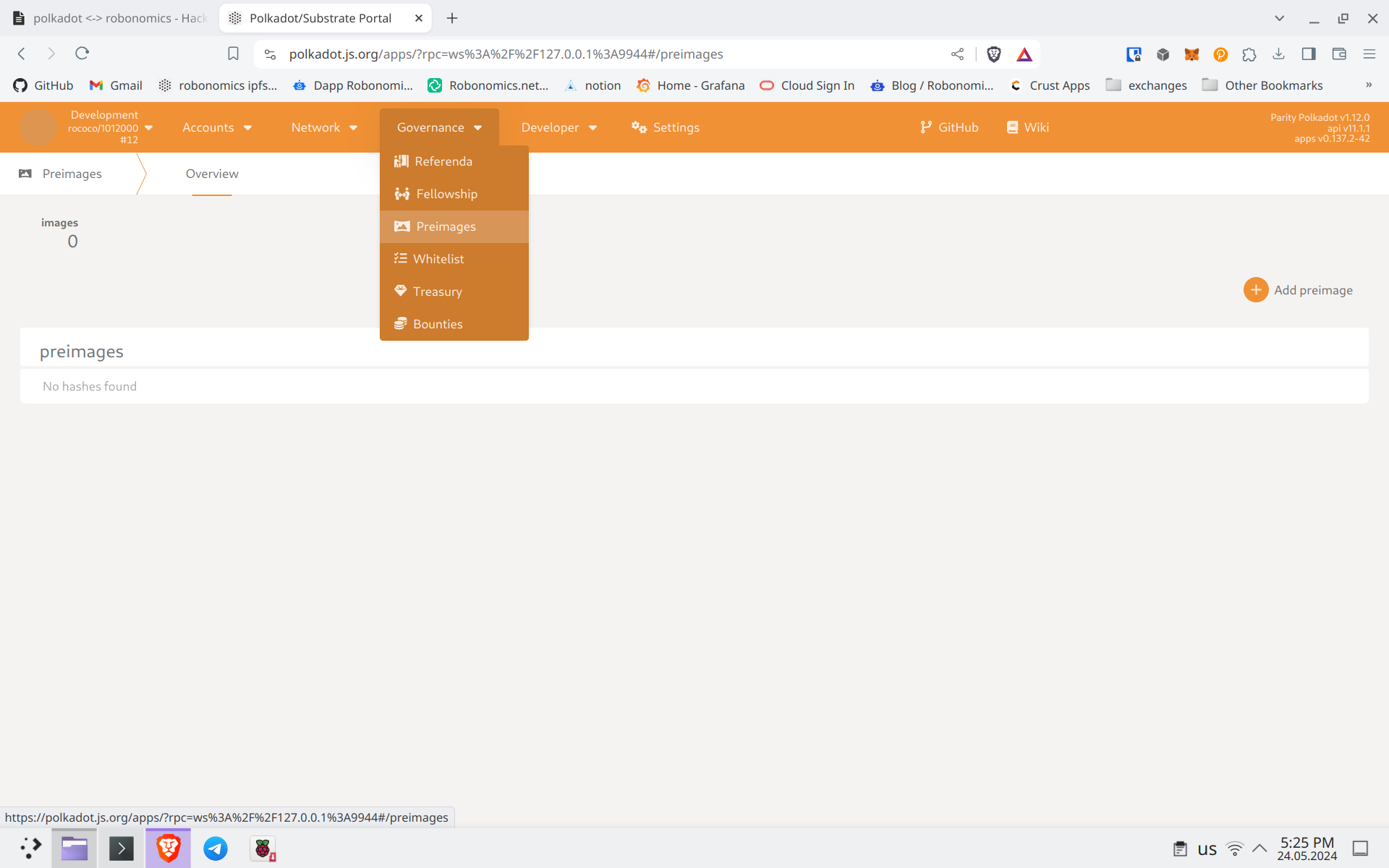
Create a new preimage. Let’s leave a remark in the network. Sign and send it to the network.
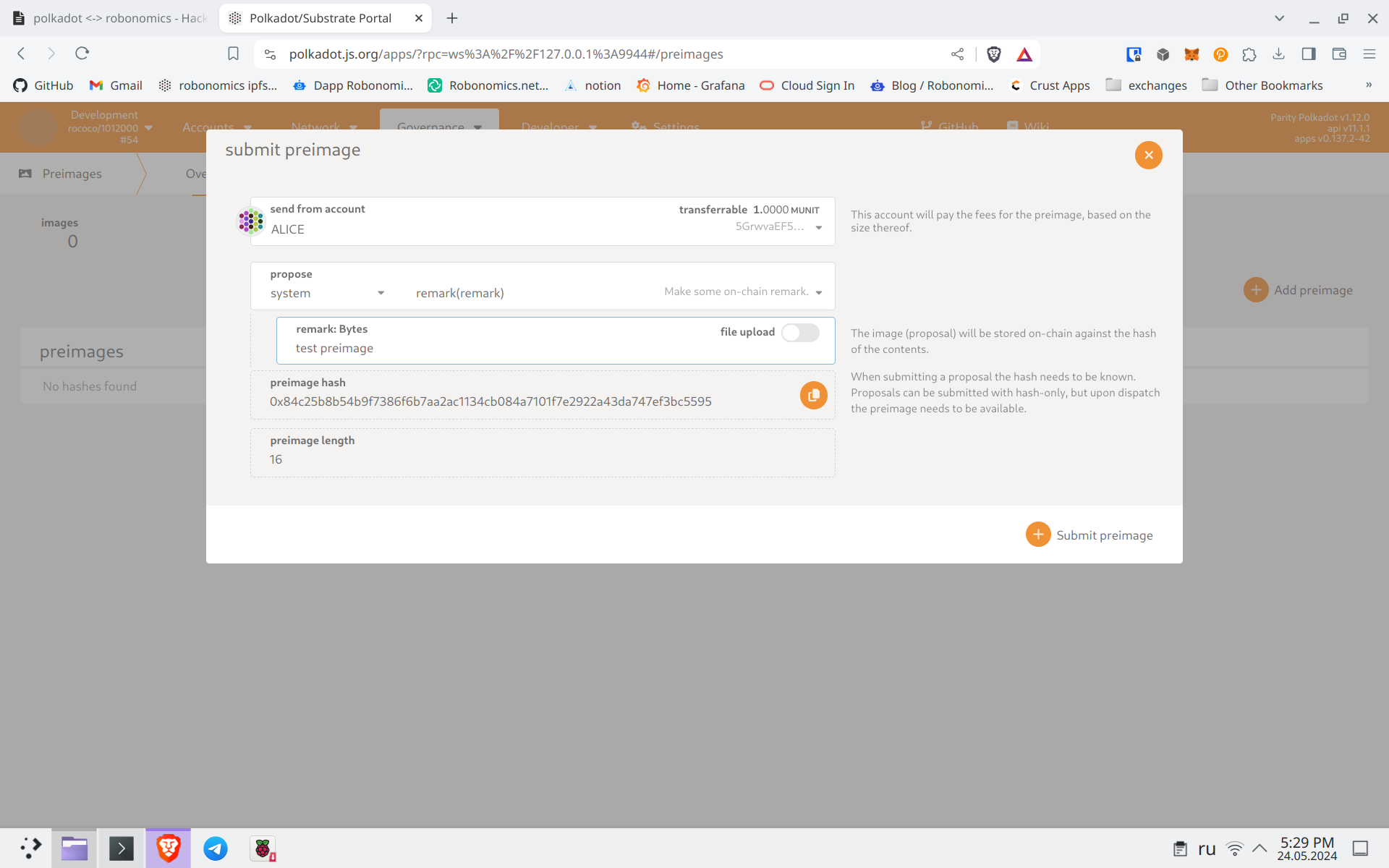
You will receive its hash. Copy it and go to the “Governance” -> “Referenda” tab. Do “Submit Proposal”. Since this is a test network, most of the configurable fields can be left as default. Paste the preimage hash and sign the proposal.
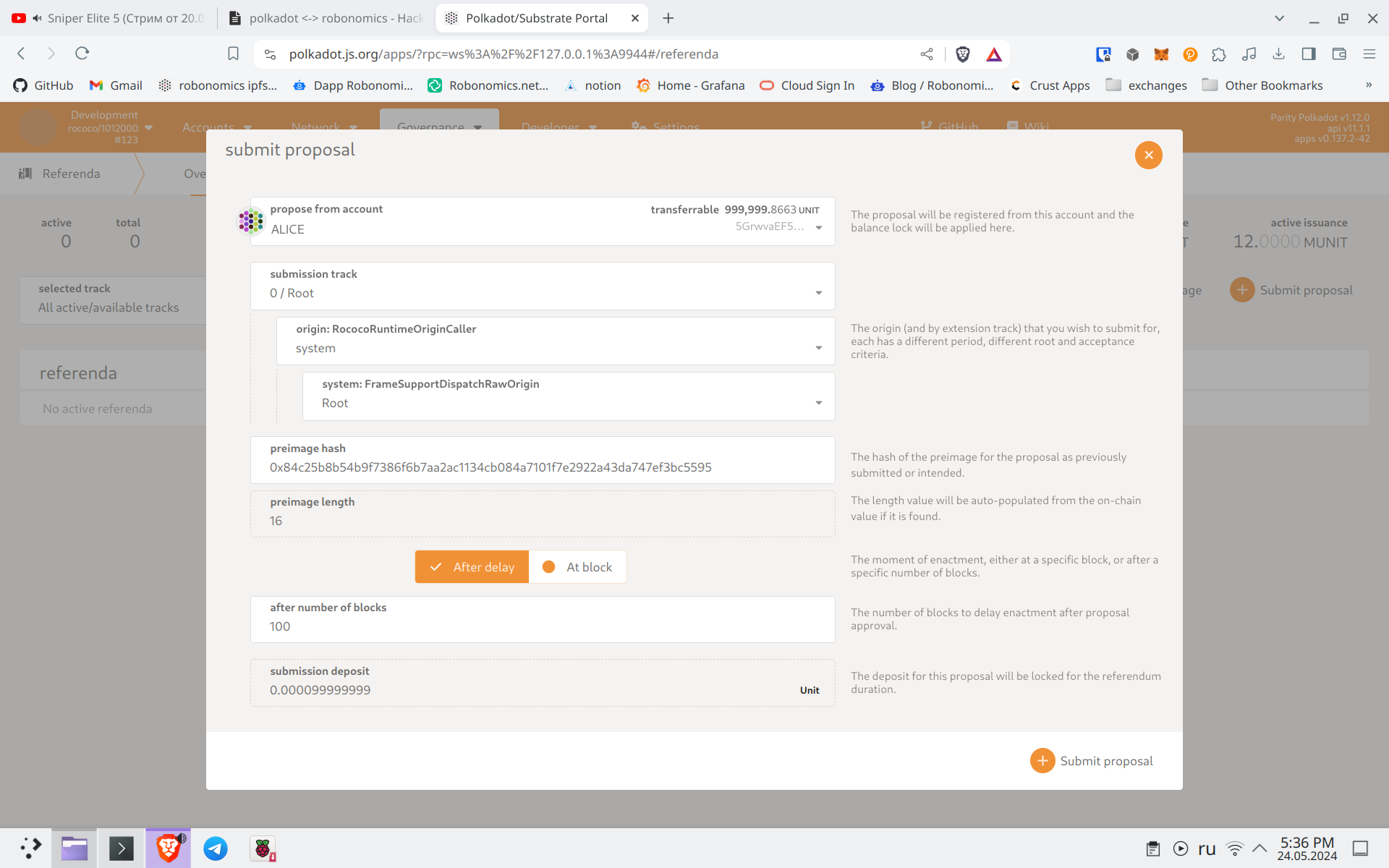
After sending it to the network, the program will detect the new proposal and output the following logs:
Referenda count start: 0
Referenda count increased: 1
Connecting to the Smart Home
Now we need to add an interaction with the smart home after creating a new proposal.
For this, we need to know the following:
- Service domain
- Service name
- Target entity
- Data - should be type “dict”
Let’s see where to find them. Open the installed Home Assistant instance. Go to “Developer Tools -> Services”, select any service and switch to YAML mode. Let’s consider the example of a switch.
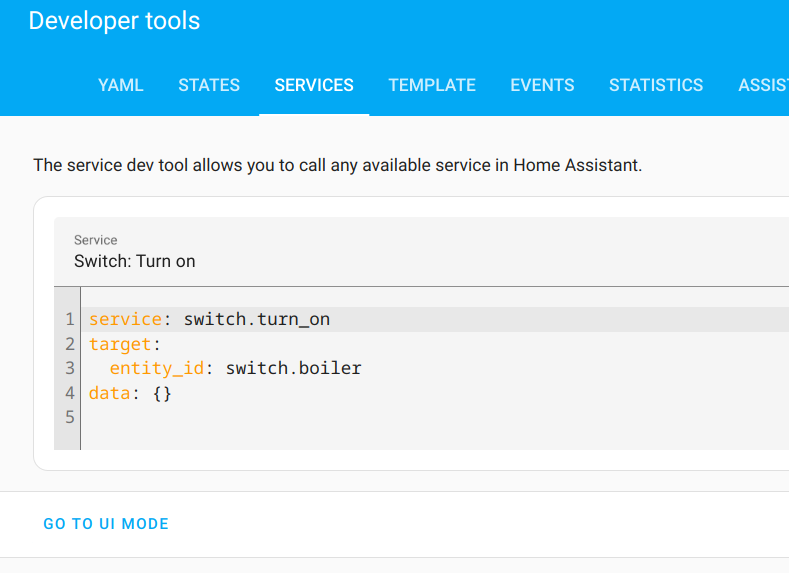
The “service” key contains the service domain and name. Everything before the dot is the domain, and everything after the dot is the service name. The data field is also needed.
To find the target entity, go to “Settings -> Devices & Services -> Entities”. There will be a column with “entity ID” - this is the required target entity parameter.
Now that we know all the parameters, let’s go through what will happen in the script.
The script will connect to the local IPFS daemon. (If you followed the smart home setup instructions, you already have the IPFS daemon running.)
First, we will form a command in JSON format. Next, the message is encrypted with the user’s and controller’s keys.
Then the encrypted command is saved to a file and added to IPFS. After that, the resulting IPFS hash is sent to the Robonomics parachain through an extrinsic Launch to the controller’s address.
When the controller receives the launch, it will download the file from IPFS, decrypt it, and call the service specified inside.
The full code is as follows:
import os
import json
import ipfshttpclient2
from substrateinterface import SubstrateInterface
from robonomicsinterface import Account, Launch
from substrateinterface import Keypair, KeypairType
from robonomicsinterface.utils import ipfs_qm_hash_to_32_bytes, web_3_auth
# polkadot part
POLKADOT_GATEWAY = "<POLKADOT_GATEWAY>" # ws://127.0.0.1:9944
substrate = SubstrateInterface(url=POLKADOT_GATEWAY)
# Robonomics part
# Robonomics credentials
# User address must be in RWS devices
# User address must be ED25519
user_seed = "<SEED_PHRASE>"
controller_address = "<CONTROLLER_ADDRESS>"
sub_owner_address = "<OWNER_ADDRESS>"
# Command
service_domain = "<DOMAIN>" # domain is what is before the dot in the name of the service. For example "switch"
service_name = "<NAME>" # name - what comes after the dot in the name of the service. For example "turn_on"
target_entity = "<ENTITY_ID>" # entity_id. For example "switch.boiler"
data = {} # Must be dict
def subscription_handler(data, update_nr, subscription_id):
if update_nr == 0:
print('Referenda count start:', data.value)
if update_nr > 0:
print('Referenda count increased:', data.value)
# Send launch to controller address with ipfs hash
launch = Launch(sender, rws_sub_owner=sub_owner_address)
res = launch.launch(controller_address, result_ipfs)
print(f"Transaction result: {res}")
def encrypt_message(
message, sender_keypair: Keypair, recipient_public_key: bytes
) -> str:
"""
Encrypt message with sender private key and recepient public key
:param message: Message to encrypt
:param sender_keypair: Sender account Keypair
:param recipient_public_key: Recepient public key
:return: encrypted message
"""
encrypted = sender_keypair.encrypt_message(message, recipient_public_key)
return f"0x{encrypted.hex()}"
# Format message to launch
data['entity_id'] = target_entity
command = {'platform': service_domain, 'name': service_name, 'params': data}
message = json.dumps(command)
print(f"Message: {message}")
sender = Account(user_seed, crypto_type=KeypairType.ED25519)
# Encrypt command
recipient = Keypair(
ss58_address=controller_address, crypto_type=KeypairType.ED25519
)
message = encrypt_message(message, sender.keypair, recipient.public_key)
print(f"Ecrypted message: {message}")
filename = "temporal_file"
with open(filename, "w") as f:
f.write(message)
with ipfshttpclient2.connect() as client:
result = client.add(filename, pin=False)
result_ipfs = result["Hash"]
print(f"IPFS hash: {result_ipfs}")
print(f"IPFS hash for launch {ipfs_qm_hash_to_32_bytes(result_ipfs)}")
os.remove(filename)
substrate.query("Referenda", "ReferendumCount", subscription_handler=subscription_handler)if you did everything correctly, you will see the following logs:
Message: {"platform": "switch", "name": "turn_on", "params": {"entity_id": "switch.boiler"}}
Ecrypted message: 0x33356b915e51e4c050180db0c3e39de86e946b6807ea83114978c848d016ab34a812e271dd1e5b40aa8632edd5acf4254090d2c2849daafcc46d2d4a4406a169a04edb4a668a268b3265e96ded0411398e3520fd5b676109752d24f12a7ece976bdc58da6a5b95d3c9e77aa59270bbc86c66c2ffe69ef7b10fae20
IPFS hash: QmcrqSD3bBYmm4rpaDMUVNQwF8CSi5WWVnwPtuGJdzgWpK
IPFS hash for launch 0xd7bf2b46baebf5556ac30fda97d7bf34a71558acdafde694c849521d01ccd8b4
Referenda count start: 0
Referenda count increased: 1
Transaction result: 0xe07d43462d540a7312763349b362318c427ca9a61e7d5bfa3c890e8b1c0294c1
